por
Robin Lasky, Contributing Reporter | March 01, 2021
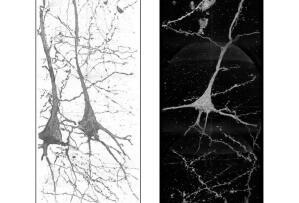
These 3D images of neurons in the brain of a schizophrenia patient show wavy, distorted neurites, which indicate that the condition may be linked to the shape of the neurons. X-ray images were taken at the Advanced Photon Source.
Use of synchrotron radiation nanotomography has allowed researchers to produce uncorrupted 3D images of neurons and blood vessels for the purposes of studying schizophrenia’s effect on brain tissue.
Schizophrenia is a chronic mental disorder which can cause a range of debilitating cognitive and psychiatric symptoms, such as paranoid delusions, depression, disordered thinking, and auditory and visual hallucinations. Despite it long being the subject of medical research, which has produced various psychiatric treatment options, Schizophrenia continues to frustrate scientific discovery into precise underlying causes. However, various genetic, environmental, and other physical factors have been identified as correlating with an increased likelihood of developing the disorder.
A new study from the University of Tokai, in Japan, in conjunction with other institutions, published in
Translational Psychiatry on January 13th, seeks to shed more light on the physical differences of brain tissue in people afflicted with this disorder, in the hopes of eventually contributing to a better understanding of its causes and impact on the brain.



Ad Statistics
Times Displayed: 56862
Times Visited: 746 Reveal Mobi Pro integrates the Reveal 35C detector with SpectralDR technology into a modern mobile X-ray solution. Mobi Pro allows for simultaneous acquisition of conventional & dual-energy images with a single exposure. Contact us for a demo at no cost.
"The current treatment for schizophrenia is based on many hypotheses we don't know how to confirm," Ryuto Mizutani, professor at Tokai University, said in a statement. "The first step is to analyze the brain and see how it is constituted differently."
For the study, four brains of deceased patients with schizophrenia were obtained, along with four healthy brains to serve as the control group. Researchers focused on an area of the brain associated with having a role in processing spoken language and other auditory stimuli.
Through the use of an advanced 3D imaging technique, they were able to discern marked differences between the structure of the neurons in the brains of patients with schizophrenia compared with the control samples that may indicate association with the disorder.
Various brain imaging systems have been used to contrast the differences between healthy brains and the brains of patients with schizophrenia in order to better understand its effects on the brain. For instance,
MR scans have been used to contrast the neuro-electrical responses to certain stimuli with that of healthy control groups. MR scans have also been used to identify and target specific areas of the brains for studies of
proposed novel treatments for schizophrenia.

